interkriti®
YOUR GATEWAY TO CRETE
|
Crete
List Grid Map
Found
119
- Showing :
41 - 60
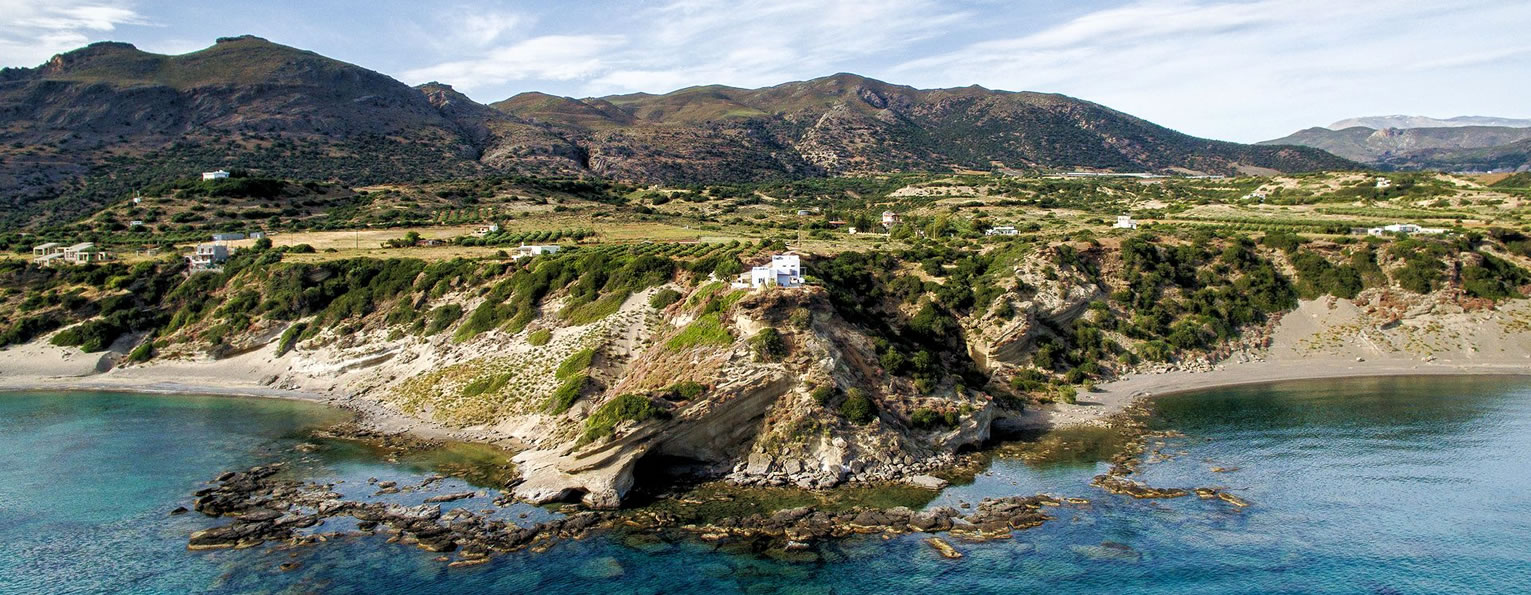
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The south end of the West Court is occupied by four large stone-built structures known as "Kouloures" (rings) ,belonging to the Old Palace complex. The workmen on Evans' excavation gave them their name when they were first discovered at Knossos. Similar pits were also later discovered at the Palace of Malia. Their exact use is unknoun, although today they are generally regarded as depositories for offerings from the Palace shrines, or granaries. In front of the Phaistos "Kouloures" passes a "Processional Causeway" which starts in the West Court. One of the "Kouloures" is cut across by a cobbled road built in later years. The well next to them belongs to the Hellenistic period (323 - 67 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The main facade of both the Old and the New Palace looked onto the West Court, off which the official entrances to the Palace opened. The facade which can be seen on a lower level belongs to the Old Palace(1900- 1700 BC). It is indented according to the rules of Minoan architecture. The lower part of the walls is constructed of massive limestone blocks (orthostats). The entrance is set into a recess in the SW corner of the court. lt consisted of a monumental porch with a large central column from which a splendid corridor, paved with gypsum slabs, led to the Central Court. This old entrance is now interrupted by the buildings of the New Palace. Higher up and 7 metres further back is the facade of the New Palace (1700-1450 BC). It is constructed of large ashlars and also has deep indentations and protrusions. There are two entrances leading to the interior of the Palace. The main entrance is on the north and consists of a monumental staircase leading to the Propylaea. The other is deeply recesed and leads via a wide corridor to the Oentral Court, crossing the West Wing of the Palace  Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The impressive staircase starting in the west Court led to the monumental Propylaea, the principal and most impressive entrance to the New Palace (1700-M50 BC). The portico consists of a central column - only the base is preserved today - flanked by pilasters. There followed a solid wall with a double opening and a colonnade of three columns. The floors of the Propylaea complex were paved with gypsum slabs which gave it a sumptuous appearance. The colonnade opens onto a large open-air light-well through which rainwater drained away. There are two accesses from the Propylaea to different parts of the Palace. The first access, in the hall with the colonnade, led via a staircase and corridors to the Peristyle and thence to the "Royal Apartments". The second, in the SE corner of the light-well, led to an inner staircase which ended in the Antechamber of the Magazines and the Central Court of the Palace. Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The magazines of the Old Palace(1900-1700 BC) occupied a large part of the West Wing immediately to the east of the West Court and extended to the lower terrace. Apart from their use as storage areas, they also appear to have housed some of the workshop activities of the Old Palace. Today most of the magazines have been filled in. One of these is the magazine with the giant pithoi (storage jars) decorated with discs and rope patterns in relief. Just east of this is a well-preserved quern installation for grinding grain. There is another well-preserved Old Palace magazine under the floor of the light-well in the Propylaea.  Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The north part of the West Wing is occupied by she large complex of the palace magazines or store rooms. It consists of the antechamber, the corridor of the magazines and the magazines themselves. The first wide hall forms the antechamber of the magazines and opens off the Central Court via a doorway with a central column and two pillars. Two other columns inside the room supported the roof. Under the floor of the antechamber was discovered the Archive Room of the 0ld Palace (l900 - 1700 BC), containing over 6.000 clay sealings, i.e. seal impressions on balls of clay, which were used to monitor the movement of the goods in the magazines(fig 1). A double doorway with a central pillar on the west side of the antechamber led to the corridor of the magazines, with a second central pillar supporting the roof of the corridor. To right and left were the ll magazines, in which the goods produced by the Palace were stored. The westernmost magazine, on the north side of thecorridor, which has been roofed over by the excavators contains tall pithoi (storage jars), one of which bears an inscription in Linear A (fig.2)
Image Library
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) Almost the whole south part of the West Wing was dedicated to the shrines of the New Palace. The main architectural types of shrine are the "Bench Shrine" and the "Lustral Basin". The first type consists of small, rectangular rooms with low benches running round the walls, perhaps to support cult objects and figurines of the deity. On some of them were found female figurines, ritual vessels and "Offering Tables" (small altars). On the walls of some rooms are incised sacred symbols, such as the double Axe and the star. The "lustral Basin" type consists of rooms which are set somewhat lower than the surrounding structures, with a few steps leading down into them. The were usually lined with slabs of gypsum, giving them a highly - finished appearance. Although it is doubtful that these structures contained water, it is thought that they were used for purification rituals. There is a third type of Minoan shrine in the S-E part of the shrine wing. Its is a room with central pillars (Square, stone - built columns) thought to be a cult area, similar to the "Pillar Crypts" of the Palace of Knossos, where the sacred pillar was worshiped by pouring libations.  Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The great Central Court is a basic architectural element of Minoan palaces and the core around which the different wings are set. It was the focus of the economic, social and religious activity of the palace, the setting for events which could be watched from the windows and balconies. The Central Court of the Palace of Phaistos was built in the time of the Old Palace (1900-1700 BC). It was also used in the New Palace with minor alterations to its orientation and dimensions. It is a rectangular paved, open area with colonnades running along both its long sides, with alternating pillars and columns which supported open colonnades.On the west side of the court, two adjoining rectangular rooms with benches, open on to the Central Court, may have been "sitting rooms" for the spectators watching the events taking place in the Central Court. In the east colonnade of the court, some stone-built benches next to a water cistern may have formed islands of rest and recreation. The stepped structure in the NW corner of the court may have been an altar for the ceremonies which were held here. The pithoi (large storage jars) in front of it were found in buildings founded in the site of the Great Court after the destruction of the Palace. Image Library
North Wing Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The North Wing is one of the most important wings of the Palace, as it is believed to have housed the "Royal Apartments". lt also contained sets of rooms, inner courtyards, corridors and staircases leading to the upper floor. The splendid gateway on the north side of the Central Court led to the complex of the "Royal Apartments". It is framed by two magnificent wooden half-columns, now reconstructed. On either side of the gateway are two niches decorated with wall paintings, in which the gate guards may have stood. Behind the gateway is a wide corridor with a drainage duct, which led to an inner courtyard, which in turn led to the "Royal Apartments" complex. The term "Royal Apartments" was established by the excavators, who followed the terminology applied by Evans to similar areas at Knossos. They are undoubtedly official apartments with particular architectural features, such as open balconies and colonnades, polythyra (pier-and-door partitions), lightwells and "Lustral Basins". The gypsum slab flooring and colourful wall paintings gave these apartments a particularly luxurious appearance.  Image Library
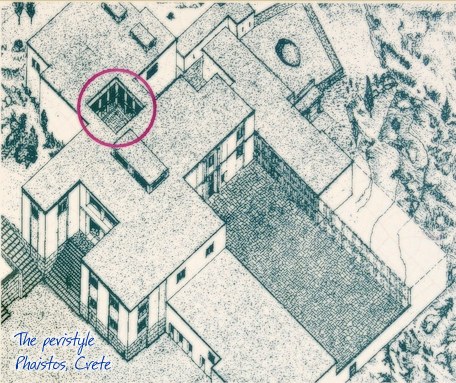
Peristyle Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The open peristyle court was one of the most elegant inner courtyards of the New Palace. It consisted of an impressive peristyle with four columns on each side supporting the corresponding colonnades, while the central area remained open. The same construction appears to have continued on the upper floor, with a second row of columns. The peristyle court was a focal point of the Palace with access routes leading from here to the "Royal Apartments", the Propylaea and the Central Court. The ruins visible on a lower level in the centre of the peristyle belong to a house of the Prepalatial settlement (3200-1900 BC).
 Phaistos Palace at 11.9km (SW) The east part of the North Wing forms the workshop area of the Palace. It consists of the East Court and a complex of small rooms which are believed to be the workshops of the New Palace (1700-1450 BC). Approximately in the centre of the court are the ruins of a horseshoe-shaped kiln. The elongated rectangular building with 6 rooms on the west side of the court appears to have been used for the workshops of the kiln craftsmen. The square room on the north side of the court was the gatehouse of the northeast entrance to the Palace. It has gypsum slab flooring and benches around the walls. Behind it is a long corridor leading to the inner courtyard of the North Wing and thence to the "Royal Apartments" Image Library
 Gortyn archaeological site at 11.9km (SE) The Hippodrome was located in the south part of the city of Gortyn, and was surrounded by columns. The central section was 374 metres long and 60 metres wide. Our information on the site is insufficient for the reason that there was never a systematic survey, or even a small excavation. What we see today of this magnificent monument are only some parts of columns and capitals.
Image Library
 Found at Phaistos Palace at 12km (SW) The disc of Phaistos is the most important example of hieroglyphic inscription from Crete and was discovered around 1903-05 in a small room near the depositories of the "archive chamber", in the north - east apartments of the palace, together with a Linear A tablet and pottery dated to the beginning of the Neo-palatial period (1700- 1600 B.C.). The disc of Phaistos can be seen at the Archaeological Museum of Heraklion. Image Library
 Malevizi, Iraklion at 12km (NE) Ano Asites (GR: Ανω Ασίτες) lies 24km from Iraklion and 6km from Agios Myron at 480m a.s.l with 423 inhabitants. A big part of the surrounding area is covered by forest on the eastern side of the mountain Psiloritis. Near the village there is the Byzantine chapel of Agios Antonios located in the ravine with the same name a place of exceptional natural beauty. From here passes the European Hiking Path (E4) which leads to the shelter "Prinos" ( of the Mountaineering Club of Iraklion - altitude 1100 m a.s.l.) located in a holly (=prinos) forest.  Malevizi, Iraklion at 12km (NE) The monastery of Aghios Georgios the Gorgolainis (GR: Αγιος Γεώργιος Γοργολαΐνι) is located on an altitude of 400 m close to the Kato Asites village. It survived through several revolutions and wars during the Ottoman occupation.  Phaistos Palace at 12.1km (SW) The church of Agios Georgios (St. George GR: Αγιος Γεώργιος) Phalandras stands a little to the south from the Palace of Phaistos on the road to Agios Ioannis village. The church was the monastery church of the Orthodox male monastery of the same name, dated to the early Venetian period (16th century), which operated normally until its dissolution in 1821. The ruins of the fortified building complex around the church were still visible until the first decades of the 20th century. Image Library
 Archaeological Site in Messara, S-W Iraklion at 12.3km (SW) The "Royal Villa" at Ayia Triada which is situated very close to Phaistos, was built in about 1550 BC. i.e. just before the new palace at Phaistos, and was destroyed by fire in l450 BC, like all other important Minoan centres. It succeeded the first palace at Phaistos as the economic and administrative centre of the regions depriving the new palace there of this role, and appears to have had connections with Knossos. The two wings, with an open-air space between them, consisted of groups of interconnecting rooms (polythyra), storerooms and stairways. On the site of the ruins, a Mycenaean megaron, the so-called "Agora" and an open - air shrine were subsequently built. In the villa's disaster layer from the fire in 1450 BC, excavation revealed a valuable group of exceptional works of art, precious materials, records in Minoan script and seals. The famous black serpentine vessels, the "Harvesters' Vase", the "Boxers' Vase" and the "Chieftain ‘ s Cup", the wall paintings depicting the natural landscape, the sarcophagus, the bronze and clay figurines of worshipers and the copper ingots from the Treasury are among the most noteworthy findings.  Kenouriou, Iraklion at 12.5km (E) Megali Vrissi (GR: Μεγάλη Βρύση) lies 32km south of Heraklion, at 620 m above sea level. In the Barozzi document of 1577, it is mentioned as forming part of the province of Monofatsi and, in the Archives of Megalo Kastro (Heraklion), it is quoted in 1583 as having 71 inhabitants; there is also a reference to the village in the Basilicata document of 1630. The Turkish census records it with 47 families in 1671, and in the Egyptian one in 1834, it figures with 27 families. In the censi of 1881 and 1900 it is mentioned as a municipality in its own right with, respectively, 240 inhabitants and 307 inhabitants. As of 1928, it becomes a commune and today it counts over 900 inhabitants. Saint Constantine is the patron saint of the village. The churches of Aghia Anna and of the Panagia Almiri are worth visiting. The Aeolian Park, one of the islands pioneering projects, has been installed in Megali Vrisi and produces electricity of 5MW.  Malevizi, Iraklion at 12.5km (NE) Kato Asites (GR: Κάτω Ασίτες lies 23km from Iraklion and 5km from Agios Myron at 450m a.s.l with 1113 inhabitants. Beautiful town with traditional architecture especially the quarters "Notiko", "Prinos" and "Kastella" close to the monastery of Gorgolaini. Other interesting sights are: The thermae of the king of Prinias, The uninhabited settlement of Nisi with traditional houses, the caves "Lesta spilios" at Marias aloni, "Astirakou spilios", "Sarakina" and "Katsivli spilios" at Lyssogremia and "Melissa", The chapels of "Panagia" aged 800 years, "Agios Antonios" aged 1000 years, "Agios Georgios" and "Agia Paraskevi". The patron Saint is "Agia Paraskevi" celebrated on the 26th July .  Messara, Iraklion South at 13km (SW) The town of Timpaki (GR: Τυμπάκι) is located in the west edge of the plain of Messara, 65.3km away from the city of Iraklion. It is a rich and busy town with significant economic activity especially due to the early vegetables production in the wider area. There are banks, a post office, medical centers, stores, schools, hotels, restaurants, ect to cover both the needs of the locals and visitors.
 Amari, Rethymnon at 13.3km (W) The village of Apodoulou is located 55 km from Rethimno at an altitude of 450m. Remains of an extensive centre of the Old Palace period (1950-1700 B.C.) have been uncovered.at the site called Gournes, near the village of Apodoulou, at the west foot of Psiloreitis. The site dominates the Amari valley and controls the main route to the Messara plain. Excavations have brought to light three building complexes while tholos tombs of the Postpalatial period (1380-1200 B.C.) have also been located in the adjacent area. The first excavations on the site were carried out by S. Marinatos in the 1930's. During World War II it was excavated by the German Archaeological Institute, under the direction of E. Kirsten. Since 1985, systematic excavations have been carried out by the Greek Ministry of Culture in collaboration with the University of Naples. The most important monuments on the site are: Building A. It lies on the east side of the hill, to the south of the massive retaining wall. It had two storeys, as is indicated by the two preserved steps of a staircase. Decades of pithoi and other vases found on the ground floor suggest that it was used for storage. The house was destroyed by fire which followed an earthquake. Building B, located to the north of the retaining wall. It is a complex of rooms which originally communicated with Building A. Building C. It lies to the east of house A and belongs to a later phase of the settlement. Tholos tomb at Sopatakia. Tholos tomb with dromos, lying to the east of the road that leads from Apodoulou to Nithavris. The dromos is 7 m. long and the chamber has a diameter of 3.10 m. Three larnakes were found inside the burial chamber. Dated to 1380-1200 B.C. Source: The Hellenic Ministry of Culture |
|||||
|
| |||||
C
O
N
T
E
N
T
S
O
N
T
E
N
T
S